The Difference Between ioT and iioT? (IOT Vs. iiOT)
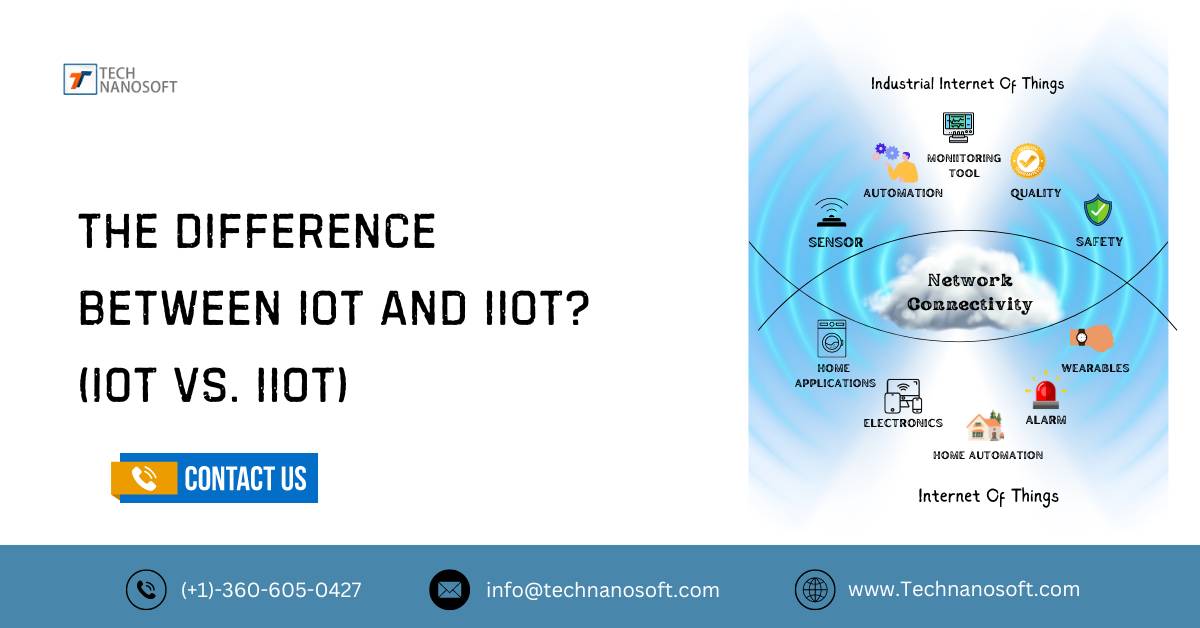
This article goes into great detail about the differences between IoT (Internet of Things) and IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things). Find out how each one changes businesses and everyday life, from the different ways they can be used to the different security and connectivity issues that come up. Learn how they affect productivity, creativity, and data management to help businesses make smart decisions about what technologies to use.
It is important to know the differences between IoT and IIoT in order to make the world of connected devices and systems easier to use, whether you are trying to improve the customer experience or make factory processes run more smoothly.
IOT Definition
The Internet of Things (IoT) is at the advance of new technology. This network connects a lot of different smart devices, from daily items like thermostats and wearable tech to industrial machinery and infrastructure. The Internet of Things (IoT) makes it possible for these devices to share info and do tasks on their own, making the world smarter and more connected.
How Does IoT Work?
IoT made up of a complex ecosystem of sensors, actuators, and communication systems. These embedded with sensors, which built into IoT devices, gather much information from their surroundings, such as human behavior and the state of the environment. After being sent through different routes, this transmit data to central hubs or cloud platforms, where advanced algorithms and analytics are used. IoT systems can take action, give useful information, and improve processes across many businesses by figuring out what this data means.
Benefits of IoT
Implementing IoT technology has many benefits in many areas, and it represents a major change in how things done. IoT improves efficiency, boosts productivity, and helps people make smart decisions by seamlessly connecting devices gadgets and systems. Internet of Things (IoT) used by companies all over the world to streamline processes, cut costs, and gain a clear competitive edge in today's market.
Also, IoT gives people unmatched convenience and control by letting them remotely monitor and handle devices from anywhere in the world, which made possible by the fact that everyone has access to the internet.
Challenges of IoT
Even though IoT has much promise, it also has some problems. With so many connected gadgets, security is becoming more and more important. This is because cyber threats and data breaches can now happen in more ways. The variety of IoT devices and standards also causes problems with interoperability, making it harder for devices to talk to each other and work together.
Additionally, keeping data private is still a big problem that needs strong security and compliance measures. To get the most out of the Internet of Things, these problems need to be solve by people from all kinds of businesses working together.
Uses and Examples of Industrial IoT
Manufacturing
IoT has changed the industrial world by making it easier to do predictive maintenance, monitor equipment in real time, and improve processes. By using IoT technology, manufacturers can learn a lot about the health of their machines, which lets them do preventative maintenance that cuts down on downtime and boosts working efficiency. This proactive method not only increases output but also makes equipment last longer, which saves much money and makes the company more competitive in the global market.
Energy Management
IoT changes the way energy is managed by giving detailed Ftraffic information and control over how energy is used in many places, like workplaces, buildings, and smart grids. With IoT enable systems, everyone can see how much energy is being use in real time, find areas where things aren't working as well as they could, and make changes to cut down on waste and costs.
IoT also supports sustainable practices by making it easier to use renewable energy sources and encouraging resource efficiency. This encourages caring for the environment and being strong in the long run when energy problems arise.
A Smart Agriculture
IoT is a game-changer in agriculture because it gives farmers actionable info to help them get the most out of their crops and resources. Farmers can see important environmental factors like soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels in real time data when they put IoT cameras in their fields.
With this information, farmers make smart choices about when to water, how much fertilizer to use, and how to get rid of pests. This will improve crop health, increase yields, and support long-term farming methods for a strong food system.
Healthcare
IoT has the potential to completely change the way healthcare is provided by allowing for remote patient tracking, personalized interventions, and proactive health management. Patients can get continuous tracking of their vital signs and health metrics from the comfort of their own homes thanks to wearable tech, smart implants, and connected healthcare platforms.
This real-time data transmission makes it easier to find health problems early, make personalized treatment plans, and act quickly, which improves patient results and lowers the cost of healthcare. IoT-driven healthcare solutions also improve access and fairness by providing healthcare services to people who don't have access to them or who live in areas that aren't well covered. This moves us closer to the goal of universal health coverage.
Key Technologies of IOT
Sensors
Sensors are the building blocks of IoT communities. They find changes in the real world and measure them. These high-tech gadgets, which include temperature and humidity sensors as well as motion detectors, collect important data that is needed for smart decisions and automatic reactions in IoT networks.
The Sensors give businesses and people real-time information about the world and how users interact with it. This information helps them improve processes, make them more efficient, and give users a more personalized experience in many areas, from smart homes to industrial automation.
Connectivity
IoT networks make it easy for devices to talk to each other and central systems over the internet. This is made possible by connectivity technologies. From the widely used Wi-Fi and Bluetooth to more specialized protocols like Zigbee and cellular networks, these connection options make it possible for devices to communicate securely, which is necessary for IoT features to work.
By connecting different gadgets and systems, connectivity technologies make it possible for people from all walks of life to work together, come up with new ideas, and create value. They usher in a time of digital transformation and interconnectedness.
Data Analytics
Data analytics is the core of IoT-driven insights. It uses cutting-edge methods like machine learning and artificial intelligence to make sense of huge amounts of data in real time. Data analytics helps people make decisions based on data by finding patterns, trends, and relationships in IoT datasets. This makes businesses more flexible and gives them a competitive edge.
Predictive maintenance in factories and personalized suggestions in e-commerce are just two examples of how data analytics can change the Internet of Things (IoT). These analytics let companies use all the data that IoT creates for strategic growth and operational greatness.
Cloud Computing
When it comes to managing IoT data, cloud computing tools are the most important part. They let you store and process huge amounts of data created by connected devices. Organizations can safely store, control, and analyze IoT data streams, no matter how big or complicated they are, by using cloud infrastructure.
This scalability not only makes real-time insights and information that can be used easier, but it also encourages new ideas and quick development of IoT apps. With cloud computing, businesses can use the power of distributed computing to get the most out of the Internet of Things (IoT). This improves efficiency, resilience, and value creation across the digital world.
Security
When it comes to the Internet of Things, security is very important because gadgets and systems that are connected are naturally vulnerable. When companies use technologies like encryption, authentication, and secure protocols, they make IoT environments safer from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
Organizations can protect private data, user privacy, and the integrity and resilience of IoT deployments by putting in place strong security measures. Security is still an important part of IoT governance, from smart homes to key infrastructure. It builds trust, reliability, and longevity in the digital age.
iiot definition
IIoT, or the Industrial Internet of Things, is a revolutionary combination of Internet of Things technology designed for use in industry, energy, agriculture, and healthcare, among other fields. iiot devices is basically connecting industrial tools, equipment, and processes to the internet. This makes it easier to collect and analyze data, which leads to better efficiency, productivity, and decision-making in industrial settings.
How Does IIoT Work?
IIoT systems are made with a complex mix of sensors, actuators, and connection options that are carefully built into industrial assets. Together, these parts get useful information from machines and processes and send it to central platforms so it can be analyzed in real-time. By using this information, businesses can improve overall performance, plan for future maintenance needs, and run their operations more efficiently. This leads to ongoing improvement and new ideas in industrial settings.
Benefits of IIoT
IIoT offers many benefits, such as a noticeable decrease in downtime, improved operating efficiency, stricter safety rules, and lower maintenance costs. IIoT helps companies get the most out of their assets by using proactive decision-making tools and predictive repair strategies. This increases the value of their assets, makes operations run more smoothly, and gives them a competitive edge in industries that are changing quickly.
Challenges of IIoT
Even though IIoT can change everything, it comes with many problems that need to be carefully thought through. Some of the biggest problems are not being able to connect different industrial systems, having weak cybersecurity, worrying about data privacy, and the need for skilled workers who know how to handle and analyze data. To fully unlock the transformative power of IIoT in driving sustainable growth and innovation within industrial sectors, we need to overcome these challenges by implementing thorough strategies, strong cybersecurity measures, and investments in workforce development.
Uses and Examples of Industrial IoT
Predictive Maintenance
IIoT changes the way factories work by bringing strategies for predictive maintenance. IIoT systems use sensors and data analytics to constantly check on the performance of equipment, finding small changes that could mean something is wrong. This proactive method lets businesses deal with problems before they get worse, which cuts down on unplanned downtime and makes key assets last longer.
Industries can improve total efficiency, lower operational costs, and make maintenance schedules more effective with predictive maintenance. This makes sure that production processes run smoothly and without interruptions. Businesses can stay ahead of maintenance problems by using IIoT for predictive maintenance. This makes them more reliable and competitive in the market.
Asset Tracking and Management
In the fast-paced world of industrial operations, keeping track of and managing assets well is essential for a business's success. IIoT solutions change the way traditional asset management is done by letting you see where assets are, what their state is, and how they're doing in real time. Industries can keep a close eye on their cars, inventory, and machines with the help of a network of sensors and tracking devices.
With this level of oversight, businesses can get the most out of their assets, make processes run more smoothly, and lower the risks of theft or loss. Businesses can be more flexible with their operations, make better use of their resources, and grow steadily in today's competitive markets by using IIoT to track and control their assets.
Smart Manufacturing
We are now in the age of smart manufacturing, which is powered by IIoT advances. This is because technology and manufacturing processes are coming together more and more. IIoT makes it possible to monitor, control, and improve industrial processes in real time by linking machines, production lines, and supply chains.
This revolutionary method improves the adaptability, speed, and output of industrial systems, leading to better operations and happier customers. Industries can quickly respond to changing market needs with IIoT-driven smart manufacturing industries solutions that make the best use of resources and shorten the time it takes to get goods to market. Using IIoT for smart manufacturing gives companies the tools they need to be more efficient, come up with new ideas, and grow in the digital age.
Energy Management
Sustainable energy management is an important part of modern business. IIoT provides useful tools for reducing waste and better caring for the environment. IIoT technologies allow businesses that use much energy to track and analyze how it is used in real time, finding inefficiencies and ways to make things better. Organizations can save energy, cut costs, and leave less of a carbon impact by using data-driven insights.
Energy management systems that are driven by IIoT not only save money but also help the environment, making the industrial ecosystem greener and more resilient. Using IIoT for energy management gives businesses the tools they need to run more efficiently and helps create a better, more sustainable future for future generations.
iiot vs iot
| S.NO |
Aspect |
IoT |
IIoT |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1. |
Focus |
consumer apps and everyday devices |
Energy, industry, and industrial uses |
| 2. |
Environment |
Varied, including homes, healthcare |
Places like workshops, warehouses, and industrial areas |
| 3. |
Purpose |
Convenience, automation, lifestyle |
Efficiency, optimization, predictive maintenance |
| 4. |
Connectivity |
Cellular, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth |
Wired (Ethernet), Wireless (e.g., Zigbee, LoRa) |
| 5. |
Security |
Standard security measures |
Better security because of key infrastructure |
READ ALSO- Innovative AI Business Ideas In Various Industries
Key Technologies of IIOT
Sensor Technology
Sensors are the most important part of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) because they collect useful data from machines and processes in factories. Sensors are made to measure many things, like temperature, pressure, vibration, and flow, giving real-time information about how assets are working and what the operating conditions are. By using sensor data, businesses can keep an eye on the health of their equipment, find problems, and make the best use of their maintenance schedules. This makes all of their processes more productive and efficient.
Edge Computing
Edge computing changes the way data is processed in the IIoT by moving computations closer to the sources of data. This method cuts down on latency and saves bandwidth, which is important for industrial areas where time-sensitive applications are used.
Edge computing lets research and decisions be made in real-time at the network's edge, which speeds up responses and makes operations more efficient. By using edge computing, businesses can find new ways to automate tasks, do preventative maintenance and get insights from data. This can lead to more innovation and competition in the digital age.
Wireless Connectivity
IIoT operations depend on wireless connectivity, which lets industrial devices, sensors, and control systems talk to each other without any problems. Technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and LoRaWAN make it possible to send data securely over long distances and in a variety of settings.
With wireless connectivity, businesses can connect their ecosystems, which lets them watch, control, and improve their processes from afar. Businesses can improve operational agility, scalability, and responsiveness by using wireless communication methods. This lays the groundwork for smarter and more connected industrial systems.
Cloud Platforms
Cloud systems are the most important part of IIoT data management and analytics because they provide flexible storage, computing power, and advanced analytics tools. These platforms offer safe and adaptable ways to store and get data from various sources, which makes it easier to get insights in real-time and make smart decisions.
Industries can use machine learning algorithms, predictive models, and data visualization tools to get useful information from huge amounts of IIoT data by using cloud platforms. With unmatched scalability and freedom, cloud-based IIoT solutions allow businesses to improve processes, spur innovation, and speed up their digital transformation journeys.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is very important for IIoT operations to keep industrial systems safe from cyber threats and to make sure that data and infrastructure are always available, correct, and private. Strong cybersecurity measures include encryption, authentication, access control, and intrusion detection systems to lower the risks of data leaks and people getting in without permission.
By putting cybersecurity first, businesses can keep private data safe, avoid downtime, and stay in line with regulations in IIoT environments that are highly connected. Strong cybersecurity procedures not only protect important assets but also build trust and dependability in IIoT ecosystems, which makes it possible for industrial infrastructures to be safe and strong.
IoT and IIoT Security
In both IoT and IIoT, security is very important, so strong steps must be taken to protect against holes, data leaks, and cyberattacks. Protocols for encryption keep data transmissions safe, and methods for authentication make sure that the device and user are who they say they are. Access control stops people who aren't supposed to be there from getting in, and regular software changes fix known bugs.
The real-time incident reaction is possible thanks to continuous monitoring and threat detection. Following industry norms makes sure that security frameworks are complete. Together, these steps protect the integrity of data, the privacy of users, and the dependability of systems in environments that are linked to each other. This builds trust and makes IoT and IoT deployments more resilient.
IoT Security
IoT security strategies include encryption, authentication, secure device provisioning, firmware updates, and secure communication methods to protect IoT operations at home and in businesses from malware, unauthorized access, and data tampering.
IIoT Security
To keep important infrastructure, private data, and industrial processes safe in IIoT settings, strict security steps are needed. To protect against cyber threats and keep operations running, this means putting in place access controls, intrusion detection systems, network segmentation, and resilient designs.
Future Opportunities in IoT and IIoT
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and the Internet of Things (IoT) both have problems. Still, they also offer many chances for growth and new ideas. Edge computing for real-time data processing, AI-driven analytics for actionable insights, blockchain acceptance for better security and openness, and 5G connectivity for fast, low-latency communication are some of the trends that could happen in the future.
Setting up industry norms will also help with issues of security, interoperability, and sustainability. This will make it easier for IoT and IIoT solutions to work together and be widely used. These improvements look like they will change businesses, make things more efficient, and lead to long-term growth in the digital age.
Understanding Your Needs For IOT
Consider your specific IoT application Factors like:
Data Volume: How much data will your devices transmit?
Latency: How critical is real-time data transmission? (e.g., remote surgery vs. fitness tracker)
Power Consumption: How much battery life do your devices require?
Device Range: How far do your devices need to communicate?
Security: How sensitive is the data being transmitted?
Industrial Demands For IIOT
Reliability: Industrial processes can't afford dropped connections or downtime. IIoT connectivity needs to be rock-solid.
Security: Industrial data is often highly sensitive. Secure communication protocols and robust encryption are paramount.
Real-Time Performance: Many industrial applications rely on real-time data for decision-making. Low latency connections are crucial.
Harsh Environments: Industrial settings can be hot, dusty, or prone to electromagnetic interference. Connectivity solutions need to be robust and withstand these conditions.
The iot Connectivity Landscape
Here's a breakdown of some prominent IoT connectivity options:
Cellular Networks (2G, 3G, 4G, 5G)
Pros: Wide coverage, reliable data transfer, supports high bandwidth applications like video streaming.
Cons: Can be expensive for large numbers of devices, higher power consumption.
Wi-Fi
Pros: High bandwidth, readily available in many locations, good for short-range communication.
Cons: Limited range of security concerns in public networks.
Bluetooth (Classic & Low Energy)
Pros: Low power consumption, suitable for short-range data transfer, widely used in wearables.
Cons: Limited range, not ideal for high bandwidth applications.
Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWANs)
Pros: Long range, low power consumption, ideal for battery-powered devices in remote locations (e.g., smart metering). Examples include LoRaWAN, Sigfox, NB-IoT.
Cons: Lower bandwidth compared to cellular or Wi-Fi.
Satellite
Pros: Global coverage, ideal for remote or unconnected areas.
Cons: Higher latency can be expensive, depending on usage.
The Importance of Integration
In the complicated world of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), systems, devices and equipment from different makers must work together without any problems. Standards for connectivity, like IO-Link and OPC UA, are very important for making this combination possible. The IO-Link standard interface for sensors and motors makes sure that they can work with each other.
It makes it easier to connect different devices. In the same way, OPC UA lets industrial control systems talk to each other safely and reliably, even if the systems are made by different companies or use different protocols. IIoT systems can achieve seamless connectivity, interoperability, and scalability by following these guidelines.
The Future of IoT Connectivity
5G Private Networks: When 5G is widely used, it will change IIoT by providing very fast speeds and stable internet connection, allowing even more advanced industrial uses.
Network Slicing: This technology lets you make virtual networks inside a real network so that different IIoT applications in the same building can get the support they need.
Deterministic networking: The new technology that tries to meet specific latency and bandwidth needs. It is important for real-time mission-critical IoT applications.
Conclusion
Technanosoft's way of integrating IoT goes beyond standard methods; they use a mix of art and technology to make connections work smoothly. Think of a tapestry with threads that are all linked to each other. Each thread represents a different part of integrating IoT. Technanosoft is putting these lines together to make a masterpiece: a symphony of new ideas and better ways of doing things.
Through their creative approach, they simplify things by putting together different instruments that work well together. As a result, there is a patchwork of connectivity, and each node and sensor is an important part of the big picture of IoT integration. With Technanosoft's artistic touch, companies go on a journey of discovery where they can see an endless canvas of possibilities.
FAQs About iot and iiot:
Q.1- What is the difference between IoT and IIoT?
A- The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of devices, sensors, and objects that are all linked together and can talk to each other and share info over the internet. IIoT, on the other hand, connects systems, machines, and tools in production and industrial settings.
Q.2- How do internet of things iot and IIoT differ in their applications?
A- IoT is used in many areas, such as healthcare, smart homes, and consumer goods. IIoT, on the other hand, is mostly used in manufacturing, energy, and transportation to improve processes and make them more efficient.
Q.3- What are the key features that differentiate IoT from IIoT?
A- IIoT devices focus on being reliable, strong, and compatible with industry standards and protocols. In contrast, IoT devices are usually made for consumer use and emphasize ease of use and accessibility.
Q.4- How does data usage differ between IoT and IIoT?
A- In IoT, data comes from personal devices like smartphones and wearable tech, and it focuses on how people connect with and choose to use devices. IIoT, on the other hand, collects data from industrial machines and tools to help us understand their performance, efficiency, and maintenance needs.
Q.5- Security issues that IoT and IIoT need to be aware of?
A- IoT and IIoT both have security issues, but because IIoT deployments are more important for industrial operations, they often need stricter security steps to protect against cyber threats, data breaches, and system weaknesses.
Q.6- How do IoT and IIoT help different industries become more digital?
A- IoT drives innovation and efficiency in consumer-facing fields like healthcare and retail. IIoT, on the other hand, is a key part of industrial automation, predictive maintenance, and supply chain optimization, all of which boost productivity and cut costs.
Q.7- Can IoT technologies be used in business settings and business settings?
A- While IoT technologies can be used in industry, IIoT solutions are made to meet the special needs and challenges of industrial settings, such as being tough, dependable, and able to work with existing industrial systems and protocols.
Q.8- What steps are taken by IoT and IIoT to make sure they can work together?
A- IoT and IIoT environments are both working on standardization and interoperability. They are doing this through groups like industrial consortia and IoT standards bodies, which aim to make it easier for different devices and platforms to talk to each other and work together.